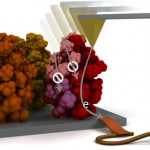
Researchers in Switzerland and Israel have succeeded in fabricating the most efficient metal oxide photoanode to date for use in photoelectrochemical cells (PECs) – devices that produce hydrogen using sunlight in a process called “water splitting”. The new feat, which involved accurately characterizing the iron oxide nanostructures used in PECs, could help in the development of much more efficient solar cells in the future……….
http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/54006