
Characterization Services
We provide various analytical services, development, research, and support for nanoscale analysis in a wide range of samples whether in physics (analysis of dimensions, shape, and surface of nanomaterials), chemical (examine the chemical composition of samples), or biological (bactericidal properties test). It can accommodate samples from industrial sectors including textile, plastics, food, medicine, cosmetics, electrical and electronics, etc. We have been standardized and certified ISO 9001 and ISO/IEC 17025. Our services are as follows:
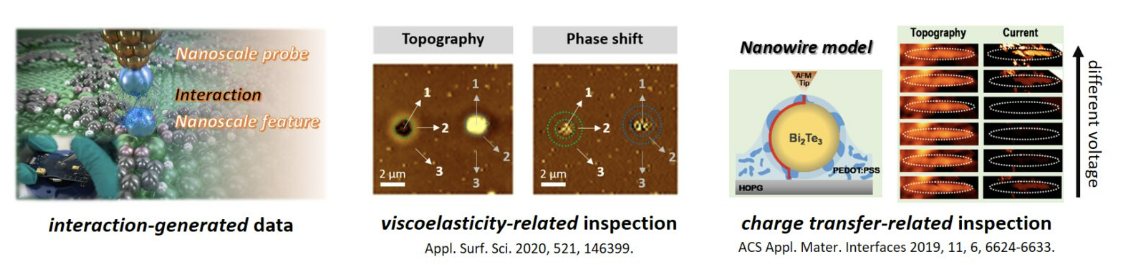
1. Atomic Force Microscope (AFM): Techniques for analyzing the physical properties of the sample surface to be measured at the nanometer scale which can study the properties as follows:
– Measurement of morphology properties :Determine flatness, roughness, height & low, measure nanoparticle size.
– Measurement of mechanical properties : resilience, surface strength at the nanometer scale.
– Measurement of electrical properties : measure current and conductivity on surfaces.
– Study the properties of samples under high vacuum conditions, heat/cool to study properties on surfaces that change with temperature as well as the measurement of dry samples and solutions such as water or buffer, etc.
2. Confocal Raman Spectroscopy : It is a technique for measuring the vibrational characteristics of molecules. This technique is laser-activated to study the chemical bond and chemical distribution on the sample surface. There are three wavelengths of light that can be used to trigger Raman scattering: blue 473 nm, green 532 nm, and red 632.8 nm. The confocal Raman spectroscopy technique can be analyzed using the modes as follows:
– Raman spectrum : measurement of Raman scattering occurring on the surface of the sample to be measured. The result is a Raman spectrum graph for further analysis.
– Raman imaging : Measurement of the Raman spectrum by scanning the area to different points on the surface of the sample to be measured. The result is chemical mapping to determine the distribution of the substance to be measured.
– confocal Raman spectroscopy : Measurement of Raman spectrum deep into the layers of the sample to be measured. It is suitable for samples with core-shell or multi-layer coating etc.
– AFM related Raman mapping : Measurement of AFM and Raman measurements in the same location to study physical and chemical properties in the same location on the sample to be measured.
confocal Raman spectroscopy can be measured either dry or wet/solid or powder. For example, carbon nanotubes, thin films, plastic sheets, natural rubber, synthetic rubber, various nanomaterials including cells and bacteria, etc.
3. Surface area and porosity (ISOTHERM/BET) : Analyze the surface area to find the diameter of the holes and the volume of the pore. The measurable example is the powder.
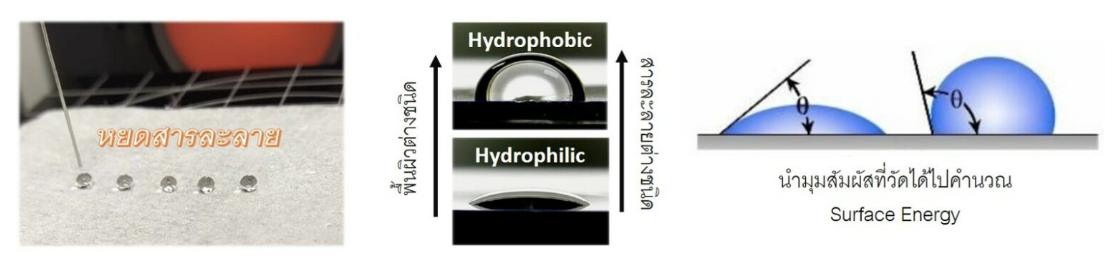
4. Contact angle : It is a technique for studying the hydrophobic and hydrophobic properties of the surface of a sample by dropping a solution such as water, alcohol, or other chemicals onto the surface and measure the contact angle that occurs. It can be applied in research such as water repellent performance analysis, automotive glass, indoor glass coating, etc. It can analyze different modes as follows.
– Measure the contact angle of water droplets, oil, or chemicals.
– Surface energy is measured by dropping at least 3 different polar solutions onto the sample surface and calculating the surface energy.
– Measure of temperature control heat stage : Study the effect of temperature on the contact angle of water droplets on the surface of the sample.
5. Field Flow Fractionation (FFF) : Field Flow Fractionation by Multi Flow Field -Flow Fractionation and Centrifugal Field-Flow Fractionation technique.
6. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) : It can achieve gains up to 1500000 times and electron acceleration up to 200 kV. It can analyze internal structure, physical characteristics, particle size and elemental composition by EDX technique.
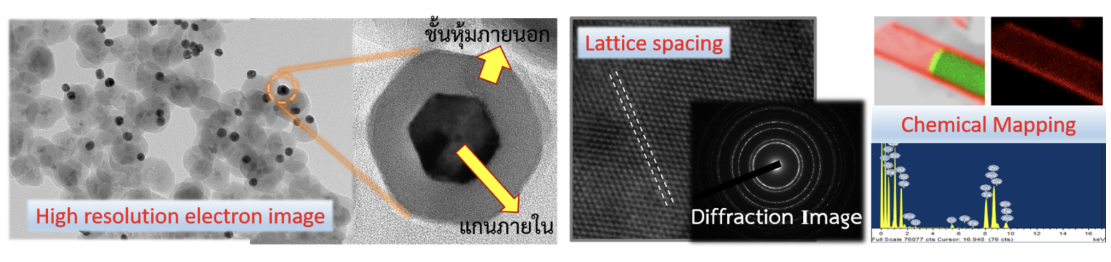
7. Environment Scanning Electron Microscope (E-SEM) : It can achieve gains up to 300000 times. Analyze structure physical characteristics and particle size
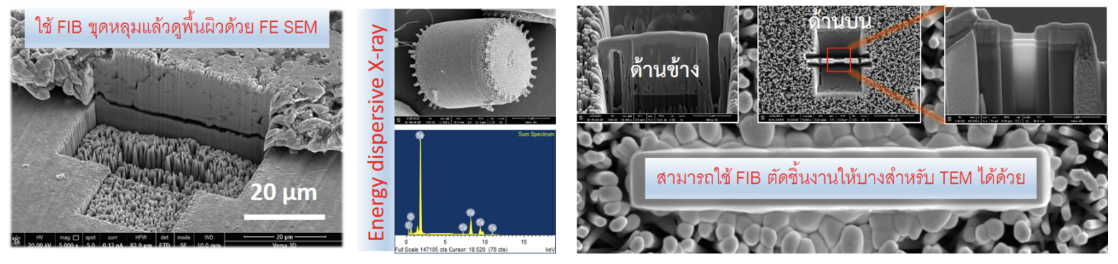
8. Focused Ion Beam and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FIB and FE-SEM): It can achieve gains up to 1000000 times and Analyze structure physical characteristics, particle size and elemental composition by EDX technique. The FIB device can cut samples with nanometer resolution for intra-material measurements.
9. Nano Coater for EM : Analyze Gold or carbon film coating samples to find conductive sample surfaces with a scanning electron microscope. In addition, the coating film can be used for other applications as well.
10. Fluorescence Stereomicroscope : A microscope that can examine organisms or specimens that can fluoresce or emit spontaneous light.
11. Fluorescence Spectrometer : Measure the fluorescence of substances by excitation from a light source and measure the light produced by emissions from emissions. The measured wavelength range is 200-900 nm. It can measure liquid samples, powders, films, plastics, acrylics, etc.
12. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) : Analyze the functional group of the sample by measuring the infrared absorption. Each function group vibrates at different frequencies reported in wave numbers.
13. GC-MS (coupling Headspace), GC-MS/MS : Analyze the type and quantity of volatile organic chemical compounds. For example, analysis of the composition of essential oils, active substances in herbs, pesticides and VOCs residues in food, packaging and the environment as well as hydrocarbon compounds from the petrochemical industry, etc.
14. HPLC, LC-MS/MS : The type and quantity of the composition of the mixture are analyzed using the separation principle to compare the results with those of the standard substance. For example, analysis of pesticide residues, food and environmental contaminants, narcotics, medical, pharmaceutical and agricultural samples as well as research on proteins and metabolites, etc.
15. Analytical Ultra Centrifuge (AUC) : The composition of the substances was analyzed during centrifugation using a rotating head detector in the wavelength range of 190 – 800 nm to analyze the motion of the particle layer, the particle laying under the centrifugal force to find Assembly and Disassembly mechanisms of biomolecular complexes, subunit stoichiometries, transformations. macromolecular conformation including particle size distribution nanoparticles with the density and molecular mass, etc.
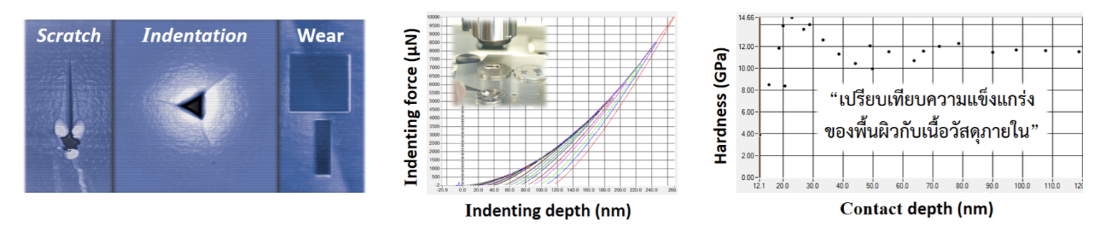
16. Nano Mechanical Tester(NMT) or Nano Indenter : It is a technique for studying the mechanical properties of samples to study stiffness, elasticity, adhesion of various nanomaterials. It can be analyzed in the modes as follows:
– Nano-indentation test : Use a small indenter at the nanometer scale – micrometer to press the sample surface to be measured with the specified force to study the strength and pressure resistance of the specimen surface or coating.
– Nano-scratch test : Drag the indenter onto the workpiece surface with the specified force to study the strength and scratch-resistance of the workpiece or coating.
– Nano-wear test : Use the indenter to drag an area with a specified pressure to study the strength and adhesion of the coating or coating of the workpiece.
– High temperature control : Able to measure the mechanical properties of the workpiece that changes with temperature
The mechanical properties of samples can be studied in both dry and wet conditions, and solid or powder samples can be measured. For example, nanometer-thin films, metal sheets, coatings of various materials, glass panels, wood panels, plastics, metal powders, powders including various types of nanomaterials, etc.
17. Weathering testing oven, Q-SUN : Simulate humidity with full humidity control and sunlight spectral range. It covers UV, visible light and infrared. It is suitable for testing the color of textiles or printing inks.
18. UV accelerated weathering tester, QUV : Simulates weather conditions for materials to deteriorate after long periods of use. It includes sun resistance, aging resistance, water resistance, corrosion resistance, cracking, discoloration, color fading. It is suitable for durability testing such as roofing, coating, plastic work, etc.
19. Mastersizer : The size of particles dispersed in solution from 10 nm to 3 mm was analyzed by measuring the intensity of the light and the angle of scattering of the light incident on the sample. It differs from DLS measurements in the sample preparation and the number of light sources. and detector
20. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), Nanosizer : Analyzed size of particles dispersed in solution from 0.3 nm to 10 µm and measure the size and particle size distribution was analyzed by measuring the intensity of light and the angle of scattering of the light projected onto the sample and the charges on the zeta potential contained in the solution.
21. Optical Microscope : It is a magnifying glass used to look at the surface of a sample on the micrometer scale. It can see the physical appearance on the surface and the crystallinity of the particles. The magnifying glass is connected to a computer and the results can be recorded for programmatic analysis of the size, width, number of particles. It can analyze samples either solid or powder and dry or wet including opaque or translucent samples
22. Tensiometer : Measure the surface tension of liquids such as cosmetics, detergents, paints, oils, chemicals, emulsions, etc.
23. Critical Point Drying (CPD) : Automated Critical Point Sample Dryer is to keep the sample in bio to dry completely.
24. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) : Analyze the stability of the material when heated. It is suitable for the analysis of samples involving gas adsorption or evaporation and crystallization due to transition.
25. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) : Analyze the thermal properties of materials, melting point, freezing point, transition, evaporation, decomposition temperature, melting energy content, and the specific heat capacity (Cp).
26. UV-Vis-NIR Spectrophotometer : Measure Absorptance, percentage of transmittance and percentage of reflectance. The measured wavelength range is 200-2000 nm.
It can measure liquid samples, powders, films, plastics, acrylics, etc.
27. ICP-MS : Analyze elements and concentration by using the atomic principle.
28. X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD), Bench Top X-Ray Diffraction Analyzer : The crystal structure of the sample was analyzed by using the X-ray diffraction principle that strikes the sample’s crystalline at different angles.
Download Supporting Documents :
Please contact us for service requests at :
Industrial Networking Development Section National Nanotechnology Center 143 Thailand Science Park, INC 2 (B) Tower Phahonyothin Road, Khlong Nueng, Khlong Luang, Pathum Thani 12120 Thailand
- 0 2564 7100 ต่อ 6517, 6625
- bitt-ind@nanotec.or.th



