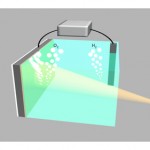
Researchers at Stanford University in the US have succeeded in fabricating a corrosion-resistant photoanode for use in photoelectrochemical cells (PECs) – devices that produce hydrogen when exposed to sunlight in a process called “water splitting”. The new electrode, which is made of a silicon-based semiconductor coated with an ultrathin layer of nickel, could help in the development of large-scale hydrogen generators in the future………
http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/55393